
Introduction :
Chatbots are AI programs created to simulate human speech. They interpret user input using natural language processing (NLP) algorithms and instantaneously deliver pertinent responses.
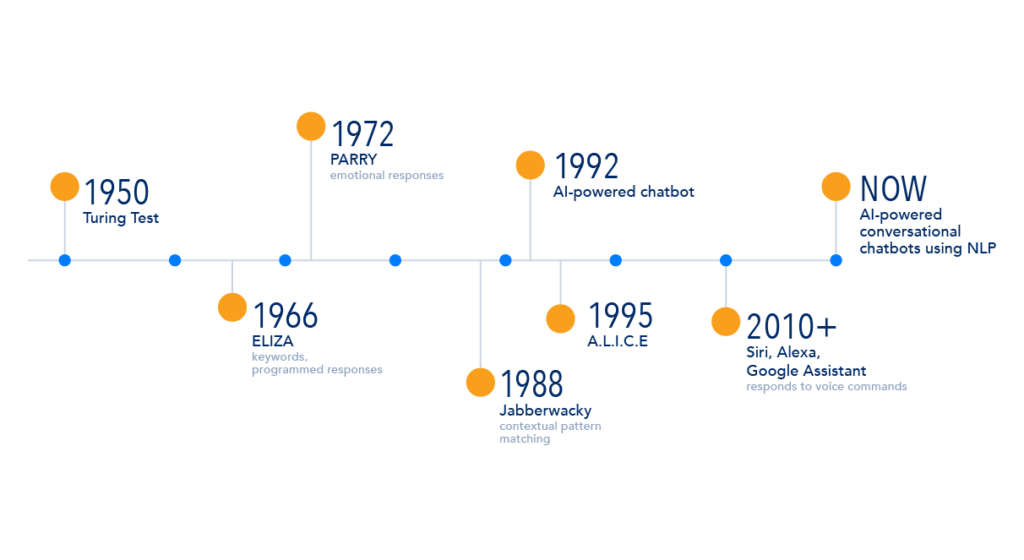
Evolution of Chatbots:
Rule-Based Systems: Chatbots’ capacity to handle complicated queries was limited in the 1960s and 1970s because they had to adhere to rigid rules and offer predetermined answers.
Scripted Responses: Chatbots began to employ more dynamic scripts in the 1990s, which enhanced interactions for particular jobs like customer support.
AI-Powered Chatbots: First released in the latter half of the 20th century, these chatbots leverage natural language processing (NLP) to comprehend purpose, context, and grow through repeated interactions.
Integration with Messaging Platforms: Chatbots became more widespread in the 2000s, automating conversations and raising user engagement on platforms like Facebook Messenger, Slack, and WhatsApp.
Recent developments in machine learning: particularly in deep learning—have improved chatbots’ capacity to analyze information, comprehend language, and customize responses.
Conversational AI: These days, chatbots are developing into conversational AI agents that can recognize linguistic nuances and modify their responses instantly.

Applications of Chatbot AI:
Customer Service : Chatbots automate customer service, answer frequently asked questions, and offer quick help on websites and mobile applications.
Healthcare and Telemedicine: Chatbots help in telemedicine consultations, medical information retrieval, and appointment scheduling in the healthcare industry.
Financial Services: With capabilities like fraud detection, chatbots in the banking industry provide virtual help for transactions and account queries in addition to enhancing security.
Technologies Behind Chatbot AI:Chatbots can comprehend and react to user inquiries in a natural way thanks to natural language processing, or NLP.Chatbots may now learn from data, customize conversations, and gradually increase the accuracy of their responses thanks to machine learning (ML).
Deep Learning: Improves chatbot performance on tasks including speech synthesis, image recognition, and sentiment analysis.
Dialog management: Organizes talks and responds to disruptions in a way that guarantees cohesive interactions.
Cloud computing and application programming interfaces (APIs): cloud computing offers scalability and performance, while APIs link chatbots to outside systems for data retrieval and task execution.

Case Studies and Success Stories:
CNN: Personalized news updates were sent by a chatbot on Facebook Messenger, which greatly increased user engagement and subscriber sign-ups.
Shopify: To help merchants with marketing, customer support, and shop administration, the company launched Kit, a virtual assistant on Messenger that will cut down on support calls and increase productivity.
Conclusion:
AI chatbots are revolutionizing customer service and operational effectiveness in many different industries. Notwithstanding obstacles, current developments indicate more innovation to come, which makes chatbots essential to improving user experience and corporate expansion in the digital age.
